Organizations, Resistance, and Democracy: How Civil Society Organizations Impact Democratization
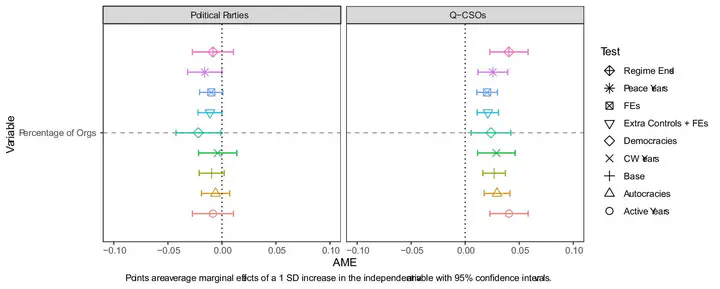 Image Generated by Authors
Image Generated by AuthorsAbstract
When are episodes of resistance likely to lead to democratization? We argue that the participation of durable organizations rooted in quotidian relationships that are not themselves designed to compete for political power (what we call “quotidian civil society organizations,” QCSOs) drives successful democratic transitions. QCSOs are more likely to have stable preferences for democracy and durable mobilization structures that create greater accountability for new elites during political transitions and thus make shifts to democracy more likely compared to movements dominated by other organization types, such as political parties. Quantitative tests using novel data on the composition of resistance movements in Africa from 1990 to 2015 support these arguments. Older QCSOs and those independent from opposition political parties and the state also appear to be the most likely to engender democratization.